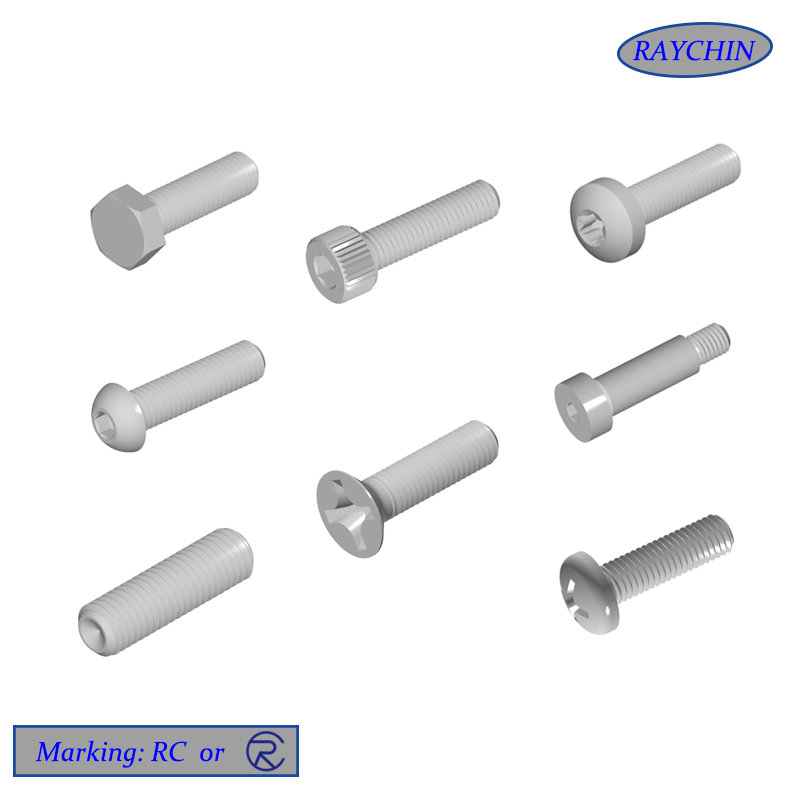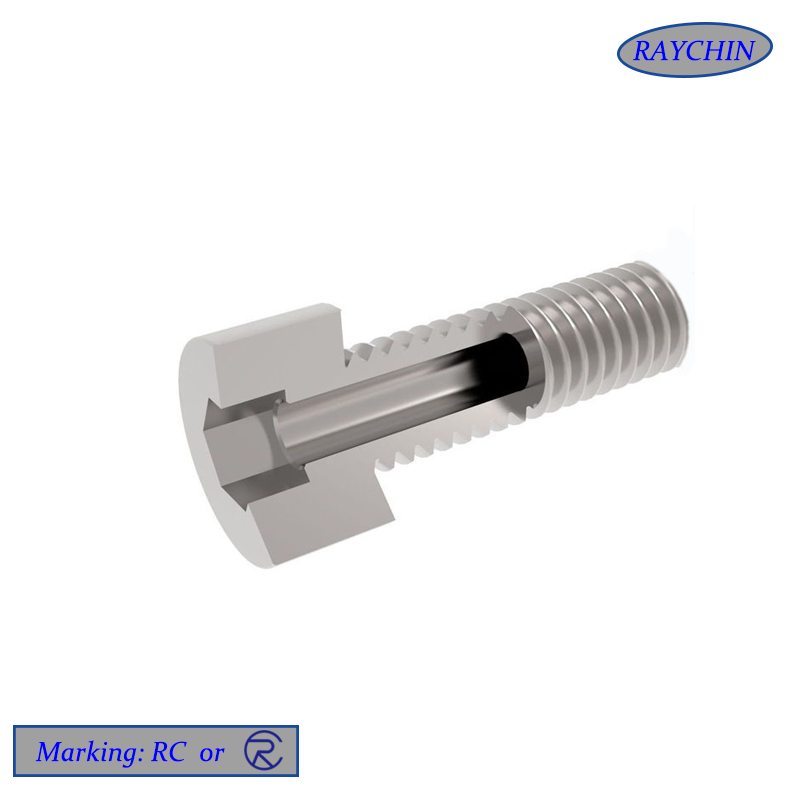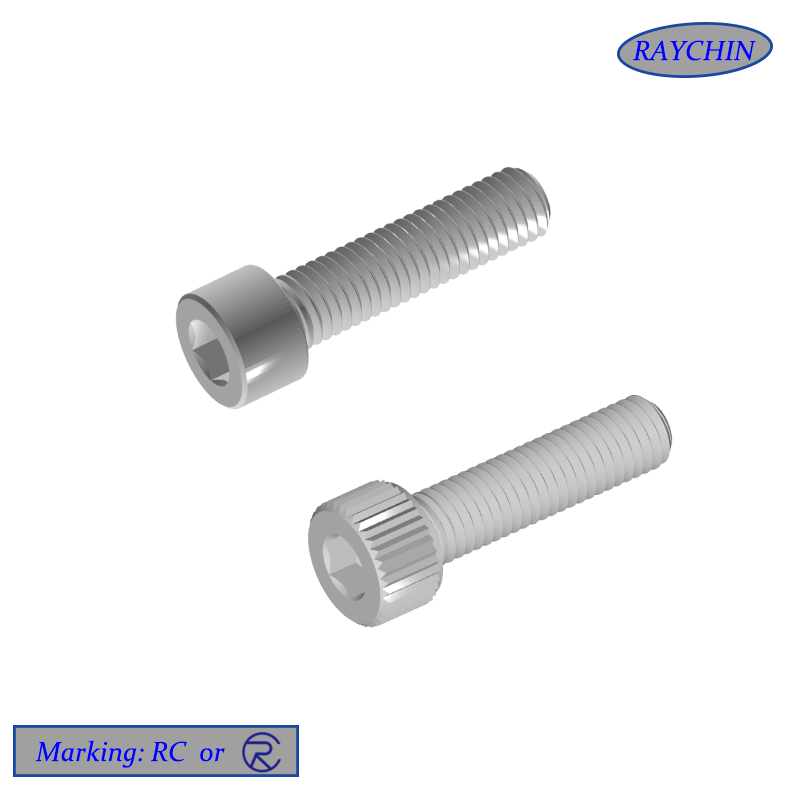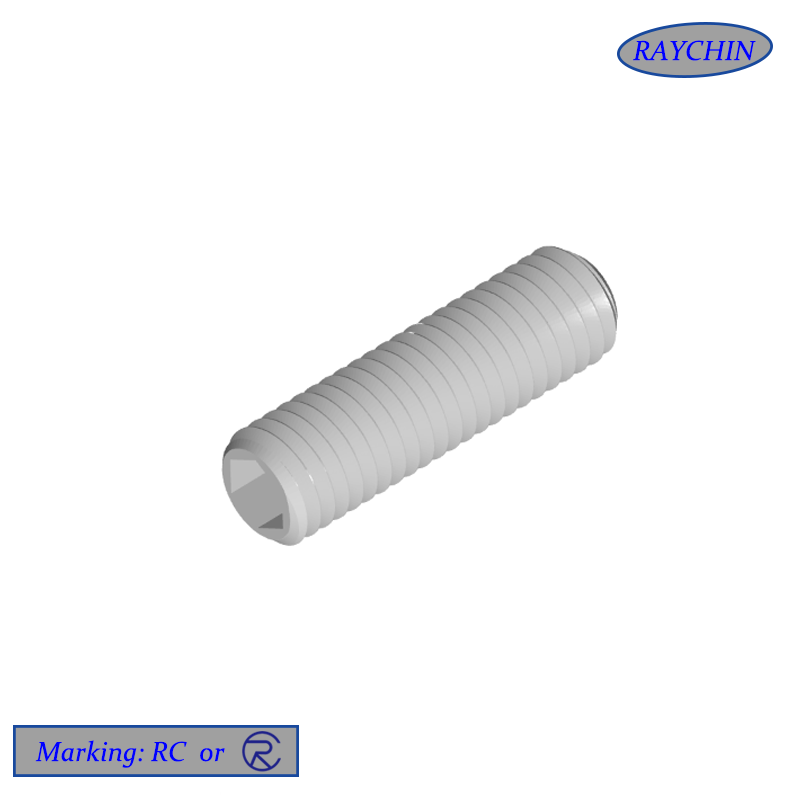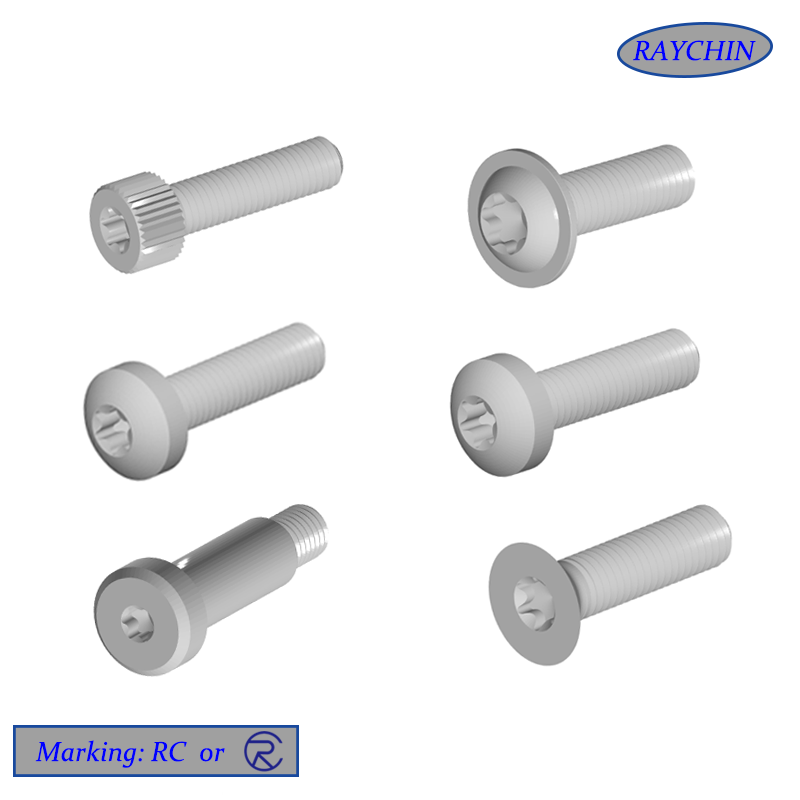
Machine Screws
Brand RAYCHIN
Product origin China
Delivery time 5-35 DAYS
Machine Screws
RAYCHIN is a manufacturer and worldwide supplier of standard & custom fasteners(Machine Screws) including those manufactured from the following materials: Hastelloy® C-276, Hastelloy® C-22, Hastelloy® B-2, Hastelloy® G-30, Monel® 400, Monel® K-500, Inconel® 600, Inconel® 625, Inconel® 718, Incoloy® A-286, Titanium Grade 2, Titanium Grade 5, Titanium Grade 7, Nickel 200, Nickel 200, Aluminum, Molybdenum, Nimonic, Nitronic, Tantalum, Tungsten, Waspaloy, Zirconium, Duplex S31803, Duplex S32205 and Super Duplex S32750, etc.
Machine Screws
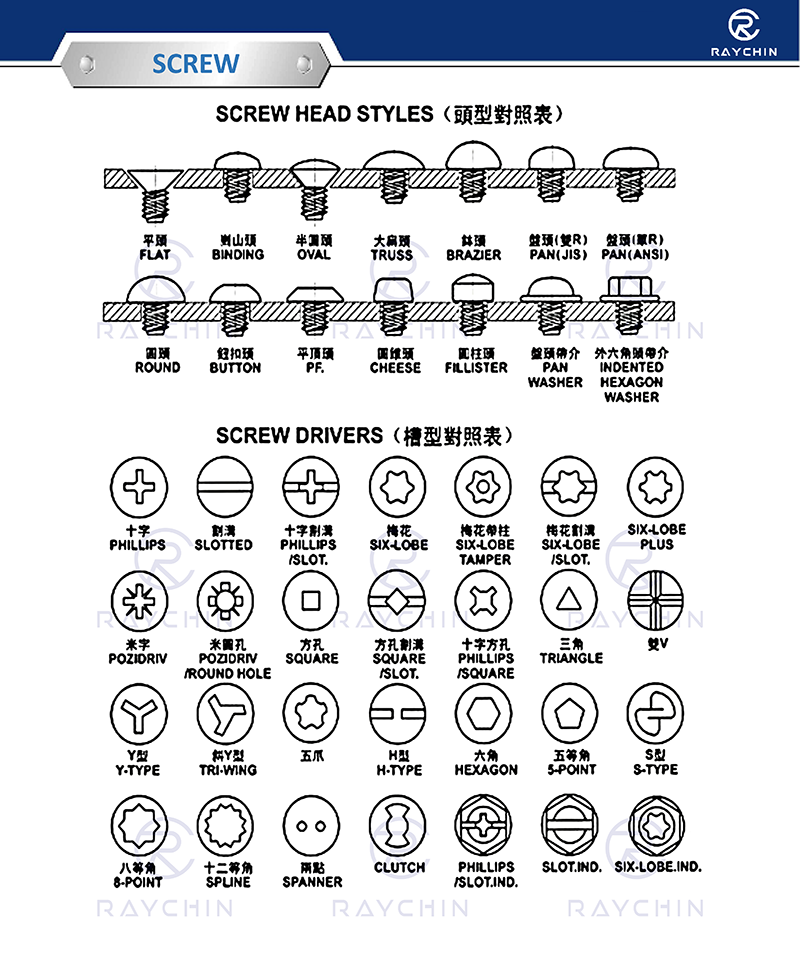
Machine screws are headed fasteners with external machine screw threads. They are commonly used with internally threaded parts and machine screw nuts. Available in coarse (UNC) and fine (UNF) threads, right-hand threads are standard (turn clockwise to tighten).
Machine screws are available in a wide array of configurations, materials, driver head types and sizes. As their name implies, machine screws are used to fasten various components together in machines, tools, appliances, electronic devices and vehicles of every description. They are available in virtually every material including steel, stainless steel.
| MATERIAL | ||||
| CARBON STEEL | ||||
| Optional materials | ||||
| 1008K | 1010K | CH10A | 1015K | CH15A |
| CH35A | CH40K | CH38F | 35ACR | 40ACR |
| CH45F | 1039 | 10B21 | 10B33 | 10B38 |
| CH35F | 1045A | CH45 | SCM435 | SCM440H |
| ML08 | ML10 | CH15A | ML15 | CH6A |
| CH8A | CH10A | CH18A | CH22A | 1022A |
| SPECIALTY METALS MATERIAL | ||||
| INCONEL | ||||
| Inconel® 600, UNS N06600, DIN EN 2.4816 | ||||
| Inconel® 601, UNS N06601, DIN EN 2.4851 | ||||
| Inconel®625, UNS N06625, DIN EN 2.4856 | ||||
| Inconel®718, UNS N07718, DIN EN 2.4668 | ||||
| INCOLOY | ||||
| Incoloy® 800H, UNS N08810, DIN EN 1.4958 | ||||
| Incoloy® 800HT, UNS N08811, DIN EN 1.4959 | ||||
| Incoloy® 825, UNS N08825, DIN EN 2.4858 | ||||
| Incoloy® 925, UNS N09925, DIN EN – | ||||
| HASTELLOY | ||||
| Hastelloy® C-276, UNS N10276, DIN EN 2.4819 | ||||
| Hastelloy® C-22, UNS N06022, DIN EN 2.4602 | ||||
| Hastelloy® B-2, UNS N10665, DIN EN 2.4617 | ||||
| Hastelloy® G-30, UNS N06030, DIN EN 2.4063 | ||||
| MONEL | ||||
| Monel® 400, UNS N04400, DIN EN 2.4360 | ||||
| Monel® K-500, UNS N05500, DIN EN 2.4375 | ||||
| NICKEL | ||||
| Nickel 200, UNS N02200, DIN EN 2.4060, 2.4066 | ||||
| Nickel 201, UNS N02201, DIN EN 2.4061, 2.4068 | ||||
| ZIRCONIUM | ||||
| Zr 702, UNS R60702, DIN EN – | ||||
| Zr 705, UNS R60705, DIN EN – | ||||
| TITANIUM | ||||
| Titanium Gr-2, UNS R50400, DIN EN 3.7035 | ||||
| Titanium Gr-5, UNS R56400, DIN EN 3.7164, 3.7165 | ||||
| Titanium Gr-7, UNS R52400, DIN EN 3.7235 | ||||
| Titanium Gr-23, UNS R56401, DIN EN – | ||||
| 6% MOLY | ||||
| AL-6XN®, UNS N08367, DIN EN – | ||||
| 25-6Mo, Alloy 926, UNS N08926 (N08925), DIN EN 1.4529 | ||||
| 254 SMO, UNS S31254, DIN EN 1.4547 | ||||
| STAINLESS STEEL | ||||
| A-286 Stainless Steel, UNS S66286, DIN EN 1.4980 | ||||
| 310S Stainless Steel, UNS S31008, DIN EN 1.4845 | ||||
| 317L Stainless Steel, UNS S31703, DIN EN 1.4438 | ||||
| 321 Stainless Steel, UNS S32100, DIN EN 1.4541 | ||||
| 904L Stainless Steel, UNS N08904, DIN EN 1.4539 | ||||
| Nitronic® 60, UNS S21800, DIN EN – | ||||
| DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL | ||||
| Duplex 2205, UNS S32205, S31803, DIN EN 1.4462 | ||||
| Super Duplex 2507, UNS S32750, DIN EN 1.4410 | ||||
| Super Duplex S32760, UNSS32760, DIN EN 1.4501 | ||||
Machine Screws vs. Bolts Although machine screws are generally considered to be smaller than bolts, machine screws also tend to be designated as such if the primary tightening of the fastened joint is accomplished by turning the head of the screw. With a bolt, the primary tightening procedure might be accomplished by turning the nut holding the bolt through a hole.
Fastening Applications Machine screws are versatile in the number of types of joints they can fasten. They can be used for fastening two or more components with through holes and a nut behind all the components. They can be passed through two or more components and then finally threaded into the rearmost component, which is solid and uniformly threaded and acts as the nut in the joint. Two opposing machine screws can also be used with threaded couplings to separate two plates or boards by the distance equal to the length of the coupling. Machine screws are also used for many types of electrical connections and terminal strips. They are also used to fasten many gasketed devices that are sandwiched together such as waterproof motor casings.
Head Types Machine screws are available in a wide assortment of driver head types, including standard slotted, Phillips head, hex socket head for use with Allen wrenches, Torx six-pointed star, square-drive socket head and security heads, which are easily driven in but very difficult to remove.
Threading Methods Machine screws may have their threads formed by die cutting, where some material is actually cut out of the grooves forming the thread, or by rolling or roll forming where the thread is rolled into the screw by precise rolling dies under very high pressure where no material is removed.