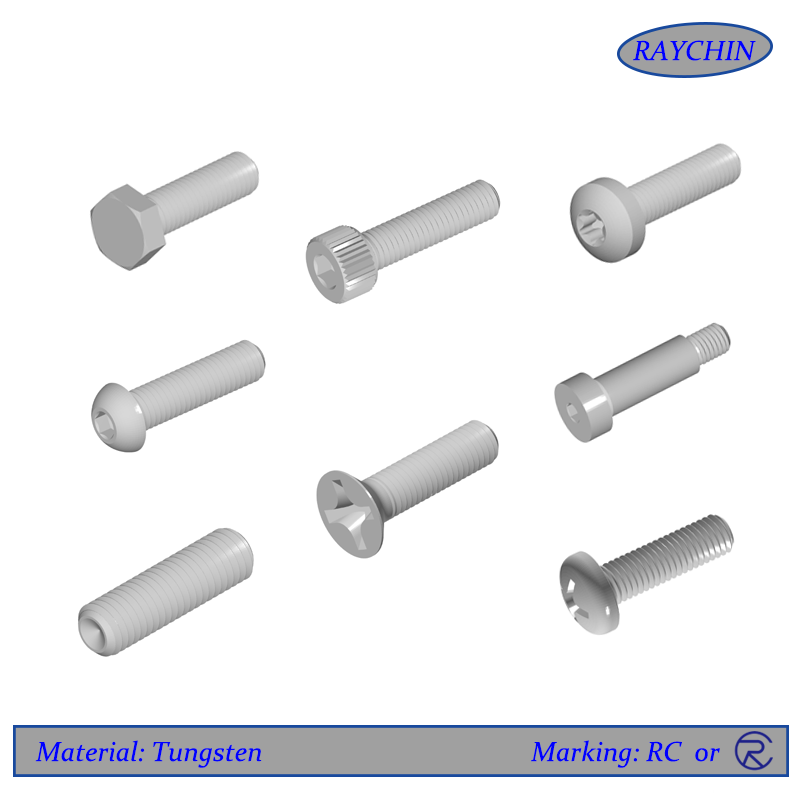
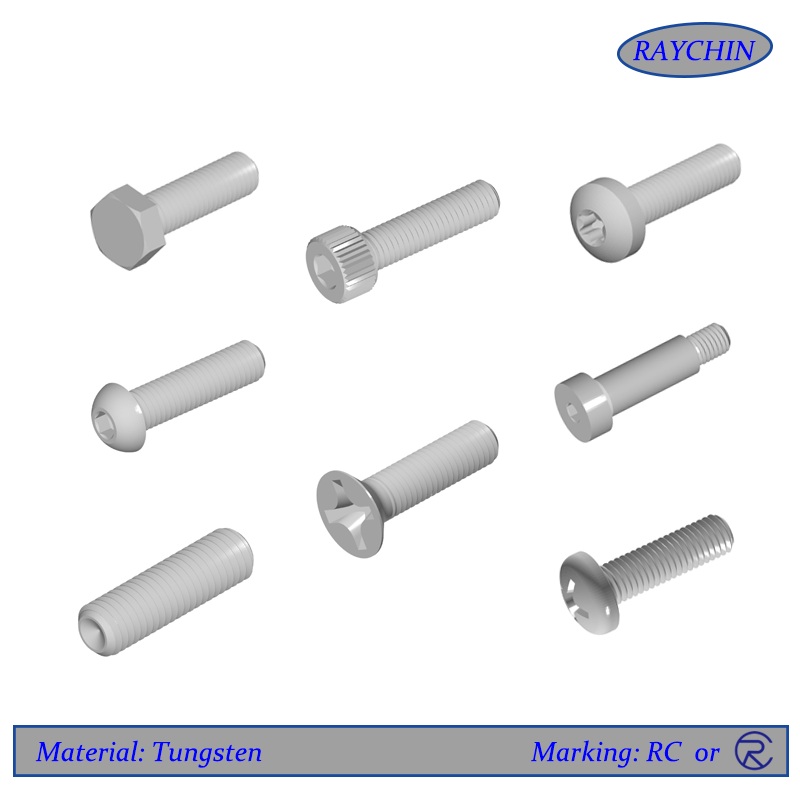
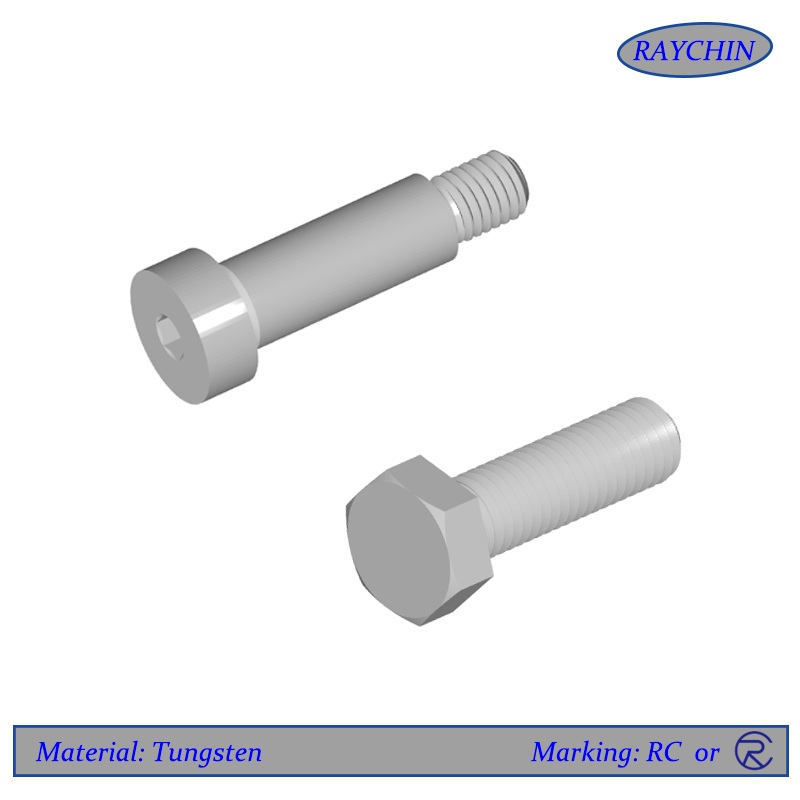
Tungsten Bolts
Tungsten Bolts
Tungsten bolts are known for their extreme high density; because of this unique attribute, they are often used for balancing rotating parts. Tungsten’s high mass also makes these bolts radiopaque. This allows tungsten bolts to block radiation and show up well on x-rays – even better than lead. Another unique attribute of tungsten is its extrmely high melting point of 3420°C. The high temperature stability of tungsten bolts make them ideal for some of the hottest vacuum furnace environments. Beyond their high mass and temperature stability, tungsten bolts are also very corrosion resistant.
Tungsten bolts are usually made from tungsten alloys per ASTM B777, and range from 90% to 97% pure tungsten, alloyed with nickel and copper or nickel and iron.
Ultra-high density & high temperature / strength stability
· Very high density of 19.3 gm/cc
· Radiopaque to x-rays and other radiation
· High strength at extreme high temperatures (vacuum)
· Excellent corrosion resistance
· Mechanical properties of tungsten bolts
· Tungsten material datasheet
Applications
· The aerospace industry depends on the tungsten bolts for their combination of high density and mechanical strength which allows them to reduce the physical size of components, offering greater control of weight distribution for propellers, inertial systems and fluid control systems to name a few.
· The heat treating / furnace industry uses tungsten bolts in high temperature vacuum furnaces due to tungstens great high temperature strength & stability.
· The oil & gas industry uses tungsten bolts for radiation shielding properties to protect equipment used in oil and gas detection, as well as down hole logging for density and ability to withstand intense hydrostatic pressure
· Tungsten bolts also play a role in the medical community for their low magnetic properties as well as their radiopaque properties.
Resources: Tungsten Torque Specs
Tungsten Bolts: Hex Bolts, Shoulder Bolts
Tungsten Chemistry & Specifications
Tungsten Specifications: ASTM B777, Mil Spec T-21014D
Tungsten Alloy ASTM-B777 | Class 1 | Class2 | Class 3 | Class 4 | CP Tungsten |
Material Composition | 90% W 6%Ni 4%Cu | 92.5% W 5.25% Ni 2.25% Fe | 95% W 3.5% Ni 1.5% Cu | 97% W 2.1% Ni 0.9% Fe | 99.95% W |
Density | 17 gm/cc | 17.5 gm/cc | 18 gm/cc | 18.5 gm/cc | 19.3 gm/cc |
Density; Ibs/in3 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.697 |
Mil. Spec. T-21014 D | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | Class 4 |
|
Type | Type II & III | Type II & III | Type II & III | Type II & III |
|
Hardness; Rockwell C | 24.0 | 26.0 | 27.0 | 28.0 | 31.0 |
Ultimate Tensile Strength; PSI | 94,000 | 110,000 | 94,000 | 100,000 | 142,000 |
Yield Strength, .2% Offset; PSI | 75,000 | 75,000 | 75,000 | 75,000 | 109,000 |
Modulus of Elasticity; PSI | 40X10E6 | 47xlOE6 | 45 x10E6 | 53 X10E6 | 58x10E6 |
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion x | 5.4 | 4.6 | 4.4 | 4.5 | 4.2 |
Electrical Conductivity; %IACS | 14 | 13 | 16 | 17 | 18 |