Inconel 718 material, head forming method of twelve-point countersunk head bolts(一)
Inconel 718 is a Ni-Cr-Fe-Nb precipitation-strengthened nickel-based superalloy. The strengthening phases are body-centered square γ'' phase and face-centered cubic γ' phase. The domestic designation is GH4169. Compared with other high-temperature alloys, Inconel 718 has good thermal stability and corrosion resistance, and has excellent fatigue and creep durability at temperatures below 650 ° C. Therefore, it has been widely used in various hot-end parts of aero-engines [1-3]. Inconel 718 twelve-point countersunk head bolt is a representative product of high-temperature and high-strength aerospace fasteners. The head is usually formed by hot heading, and the deformation of the head is relatively large during processing. Due to the complex alloy phase composition and various structures of Inconel 718 material, the process plasticity is poor, and the deformation resistance during hot working is relatively large, so the difficulty of hot forming is increased. Especially for twelve-point countersunk head bolts with countersunk head cones, the complex head shape further aggravates the inhomogeneity of the temperature field during thermal processing, making the stress distribution characteristics more complicated than conventional twelve-point countersunk head bolts. The processing performance deteriorates, and it is difficult to guarantee the size, metallographic and performance requirements of the parts. In this paper, aiming at the material properties and structural characteristics of Inconel 718 twelve-point countersunk head bolts, the processing quality of the head forming is improved by adjusting the mold structure and heating temperature of the hot heading process, and at the same time, the key dimensions of the head are guaranteed by the turning process to improve the bolt Production efficiency and pass rate to ensure the smooth delivery of the parts.
2 Product Features
2.1 Product structure and performance characteristics
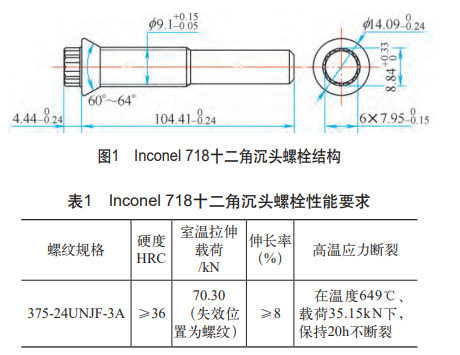
In the global bidding of an international civil aviation company, an order for a certain type of twelve-point countersunk head bolt was obtained. The part structure is shown in Figure 1, and the performance requirements are shown in Table 1. The head of the part is composed of a twelve-point head and a countersunk face. The twelve-point head can ensure uniform force during wrenching and prevent the wrench from slipping. The angle of the countersunk face of the part is 60°~64°, and the diameter of the outer circle is 14.09+0-0.24mm. Due to the complex shape of the bolt head and high machining accuracy requirements, it is difficult for the dodecagonal head and the countersunk head to meet the dimensional accuracy requirements of the part when the head is processed by the hot heading process.
2.2 Material properties and forming Difficulties
Inconel 718 superalloy has complex alloy phase composition and various structures, which reduces the process plasticity during hot working and makes the material very sensitive to changes in hot working process parameters. A higher deformation temperature can obtain uniform and fine recrystallized particles, but if the deformation temperature is too high, the cooling time after deformation will be prolonged, and the high temperature residence time will also cause the grains to grow abnormally, thus affecting the mechanics of the part performance. In addition, for Inconel 718 twelve-point countersunk head bolts with complex head shapes, there is an obvious temperature gradient during hot working. When the deformation temperature is too low, it will lead to the risk of insufficient filling of the head.
3 Analysis of processing technology
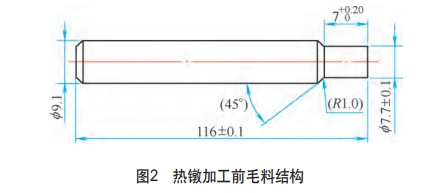
In order to ensure that the finished product meets the requirements of the drawing, the bolt head can only be formed by upsetting once, and the upsetting and forging ratio should be reduced as much as possible to facilitate the forming. According to the outer circle size of the countersunk face part, a φ9.1mm bar is selected for processing. Since the distance across sides of the dodecagonal head part is 7.95mm, it is impossible to directly use φ9.1mm wool for upsetting, so the material diameter of the dodecagonal head forming part needs to be turned to φ7.7mm. The wool structure before hot heading is shown in Figure 2.
Through the above process analysis, the main process route of the bolt is formulated: blanking→grinding→turning→hot heading→solution→turning end face and polished rod→grinding polished rod, rolling thread diameter→marking→cold rolling fillet→rolling thread→aging →Fluorescent magnetic particle detection→Performance and metallographic structure detection→Packaging.
3.2 Hot heading process
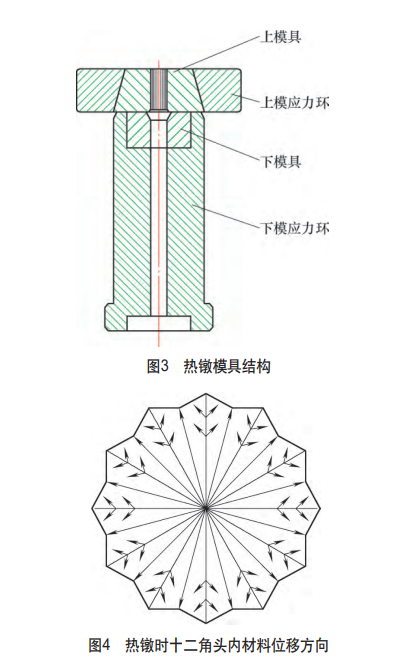
(1) Hot heading die According to the bolt structure and size characteristics, a hot heading die with a combination of upper and lower dies is used, and the structure is shown in Figure 3. Among them, the upper mold is a 12-point mold, the lower mold is an angled platform, and the end surface is the parting surface of the upper and lower molds.
When this mold is used for upsetting, it often occurs that the filling of the twelve corners of the head is not full, and the parts cannot meet the requirements of the drawing. According to the minimum resistance theorem, when the metal material is plastically deformed, the internal particle moves along the direction of the minimum resistance, that is, the particle moves to the shortest normal direction of the deformed surrounding area, as shown in Figure 4. For the dodecagonal head type, since the normal length toward the concave corner is shorter than that of the convex corner, the resistance of the mass point to the concave corner displacement is smaller, resulting in less metal material displacement in the convex corner direction, and the convex corner is thermally upset. The filling is not full. By changing the deformation speed of the material, the resistance of the material to the displacement of the lobe can be reduced, but when the deformation speed of the material is too fast, the impact force during deformation is too large, which will obviously increase the wear speed of the mold and shorten the service life of the mold. At the same time, excessive deformation speed will cause uneven deformation of the material, resulting in local cracks in the part, so it is necessary to adjust the deformation speed of the material reasonably.
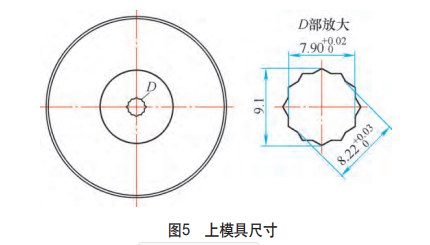
Based on the above reasons, the concave corner distance of the upper die is adjusted to φ8.22 + 0.03 -0 mm (see Figure 5), the stress during hot heading is changed, and the pre-deformation process is increased to reduce the deformation speed. Through several on-site upsetting tests, the diagonal distance of the twelve-cornered head of the part was measured, and the test results are shown in Table 2.
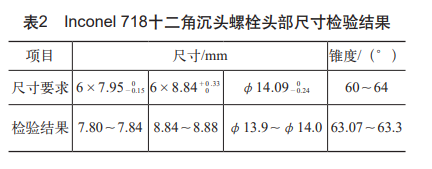
The results show that the effect of hot heading is improved by adjusting the die gap, which solves the problem of the incomplete shape of the dodecagonal head, and can ensure the head size requirements of the part.